Transportation is changing fast. More and more people are using electric vehicles (EVs) that run on batteries instead of gas. But where does the electricity come from? This article talks about different ways to make electricity from renewable energy sources.
These are sources that do not run out and do not harm the environment. Some examples are solar energy, wind energy, and hydrogen energy. We will learn how these sources can power EVs and what are the good and bad things about them. This way, we can see how they can help us have a better and cleaner future.
The Rise of Electric Vehicles
Some people like to drive electric cars (or EVs for short) because they are good for the planet and have cool features. Electric cars are different from regular cars that use gas. Electric cars do not make any smoke from their pipes, so they do not pollute the air.
But electric cars need to get power from somewhere. Sometimes, the power comes from things that are not good for the planet, like coal or oil. So, the way we get the power for electric cars is important to know how green they really are.
Benefits of Electric Vehicles
- Zero Emissions: EVs produce no direct emissions, reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Energy Efficiency: Electric motors are more efficient than internal combustion engines, converting more energy from the battery to power the vehicle.
- Lower Operating Costs: EVs have fewer moving parts, leading to lower maintenance costs and fuel savings.
Renewable Energy Sources for EVs

To maximize the environmental benefits of EVs, it is essential to use renewable energy sources for charging. Renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower offer sustainable and clean alternatives to fossil fuels.
Solar Energy
Solar energy is one of the most accessible and widely used renewable energy sources. Solar panels can be installed on homes, businesses, and even EV charging stations to generate electricity.
- Advantages:
- Abundant and renewable
- Reduces reliance on the power grid
- Low operating costs
- Challenges:
- Initial installation costs
- Weather-dependent energy production
Wind Energy
Wind energy is another viable option for powering EVs. Wind turbines convert kinetic energy from the wind into electricity, which can be used to charge EVs.
- Advantages:
- Renewable and sustainable
- High energy output in windy areas
- Challenges:
- Requires specific locations with consistent wind
- Visual and noise impact on the environment
Hydropower
Hydropower generates electricity by harnessing the energy of flowing water. It is a reliable and consistent source of renewable energy.
- Advantages:
- Consistent and reliable energy production
- Low greenhouse gas emissions
- Challenges:
- Environmental impact on aquatic ecosystems
- High initial infrastructure costs
Hydrogen Fuel Cells
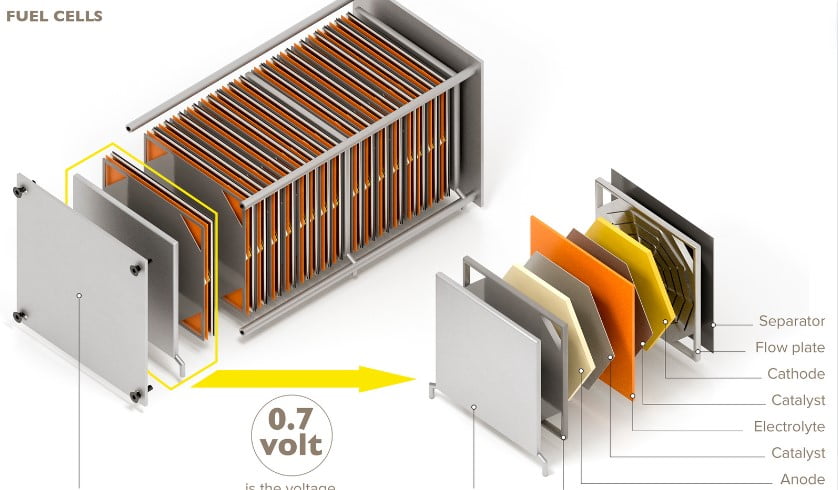
Hydrogen fuel cells represent a promising alternative to traditional batteries for EVs. These cells generate electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, producing only water vapor as a byproduct.
How Hydrogen Fuel Cells Work

Hydrogen fuel cells convert hydrogen gas into electricity through an electrochemical process. The key components include:
- Fuel Cell Stack: Converts hydrogen and oxygen into electricity.
- Hydrogen Tank: Stores hydrogen gas.
- Electric Motor: Powers the vehicle using electricity from the fuel cell.
Benefits of Hydrogen Fuel Cells
- Zero Emissions: Produces only water vapor and heat.
- Fast Refueling: Hydrogen tanks can be refilled in minutes, similar to gasoline vehicles.
- Long Range: Comparable to traditional vehicles, making them suitable for long-distance travel.
Challenges of Hydrogen Fuel Cells
- Hydrogen Production: Producing hydrogen in an environmentally friendly way is challenging and energy-intensive.
- Infrastructure: Limited hydrogen refueling stations are available.
- Cost: High production and storage costs.
The Role of Smart Grids
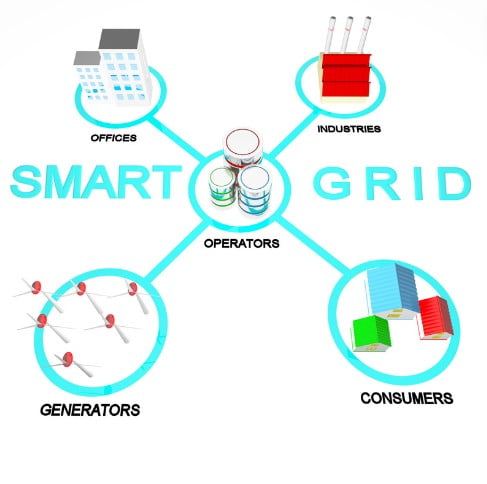
Smart grids are advanced electrical grids that use digital technology to monitor and manage the flow of electricity. They play a crucial role in integrating renewable energy sources and managing the increased demand from EVs.
Benefits of Smart Grids
- Efficient Energy Management: Balances supply and demand, reducing energy waste.
- Integration of Renewables: Facilitates the use of solar, wind, and other renewable sources.
- Enhanced Reliability: Improves grid stability and reduces the risk of outages.
Overcoming Challenges
While the transition to renewable energy and alternative fuels presents numerous benefits, several challenges must be addressed to ensure widespread adoption.
Infrastructure Development
Developing the necessary infrastructure for renewable energy and alternative fuels is critical. This includes:
- Charging Stations: Expanding the network of EV charging stations powered by renewable energy.
- Hydrogen Refueling Stations: Increasing the availability of hydrogen refueling stations.
- Grid Upgrades: Enhancing the power grid to support increased demand and integrate renewable sources.
Cost and Accessibility
Reducing the costs associated with renewable energy and alternative fuels is essential for widespread adoption. This can be achieved through:
- Government Incentives: Providing subsidies, tax credits, and grants to support renewable energy projects and EV purchases.
- Technological Advancements: Investing in research and development to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Public Awareness and Education
Raising awareness about the benefits of renewable energy and alternative fuels is crucial. This can be done through:
- Public Campaigns: Promoting the environmental and economic benefits of EVs and renewable energy.
- Educational Programs: Providing information and resources to help consumers make informed decisions.
Conclusion
Transportation means how we move from one place to another. We can use different kinds of energy to power our vehicles, like gas, electricity, or solar power. Some kinds of energy are better for the planet than others.
Electric vehicles use electricity instead of gas, so they do not make the air dirty. But we need to make sure the electricity comes from clean sources, like wind, water, or the sun. These sources are called renewable energy because they never run out.
If we use more renewable energy, we can help the planet by making less greenhouse gases. Greenhouse gases are bad because they make the earth too hot. To use more renewable energy, we need to solve some problems, like building more places to charge electric vehicles, making them cheaper, and telling more people about them.
If we can do these things, we can make the world a better place with cleaner air and less pollution.